frida 代码结构:frida-core: Frida core library intended for static linking into bindingsfrida-gum: Low-leve……
frida 代码结构:
frida-core: Frida core library intended for static linking into bindings
frida-gum: Low-level code instrumentation library used by frida-core
bindings:
frida-python: Frida Python bindings
frida-node: Frida Node.js bindings
frida-qml: Frida Qml plugin
frida-swift: Frida Swift bindings
frida-tools: Frida CLI tools
capstone: instruction disammbler
frida-gum 解析:
frida-gum 本身就是一种跨平台的设计. 有两个点需要处理统一: 1. 针对 CPU 架构的代码 2. 针对操作系统 (Backend) 的代码. 同时要在这两个点上构建 CPU/OS 无关代码, 以及规定一些统一的接口.
frida-gum/gum/arch-* 定义的是与 CPU 架构有关的代码, 也就是汇编级操作, 比如汇编指令的读 / 写 / 修复.
frida-gum/gum/backend-* 分两种情况: 1. 定义的是与操作系统有关的代码, 更多是一些内存 / 进程等操作 2. 对 arch 层级代码的封装成统一逻辑
frida-gum/* 对 arch 和 backend 的抽象封装成上层的平台 / 架构无关代码.
frida-gum/bindings/gumjs/:
分 V8 和 Duktape 两个引擎,实现了 Module、Memory、NativeFunction 等功能(
https://www.frida.re/docs/javascript-api/)
两种模式
- attach 模式
attach 到已经存在的进程,核心原理是 ptrace 修改进程内存,如果进程处于调试状态(traceid 不等于 0),则 attach 失败 - spawn 模式
启动一个新的进程并挂起,在启动的同时注入 frida 代码,适用于在进程启动前的一些 hook,如 hook RegisterNative 等,注入完成后调用 resume 恢复进程。
frida-java 解析
源码结构
index.js:
vm VM 虚拟机的 wrapper
classFactory class 的 wrapper
available 逻辑变量, 指明当前的进程是否载入了虚拟机
androidVersion 当前版本号
enumerateLoadedClasses 枚举所有加载的类
enumerateLoadedClassesSync 上面那个 API 的同步版本, 载入完毕才将所有的类作为一个数组返回
enumerateClassLoaders Android N 以上的支持
enumerateClassLoadersSync 同上
classFactory.js:
use: 找到类
implementation: 实现一个函数
overloads:
$new $alloc $init
vm.js:
getEnv
perform
attachCurrentThread
DetachCurrentThread
android.js
/global Memory, Module, NativeCallback, NativeFunction, NULL, Process/
getApi
ensureClassInitialized
getAndroidVersion
getAndroidApiLevel
getArtMethodSpec
getArtThreadSpec
getArtThreadFromEnv
withRunnableArtThread
withAllArtThreadsSuspended
makeArtClassVisitor
makeArtClassLoaderVisitor
cloneArtMethod
env.js
JNIEnv 的 wrapper
Hook 分析
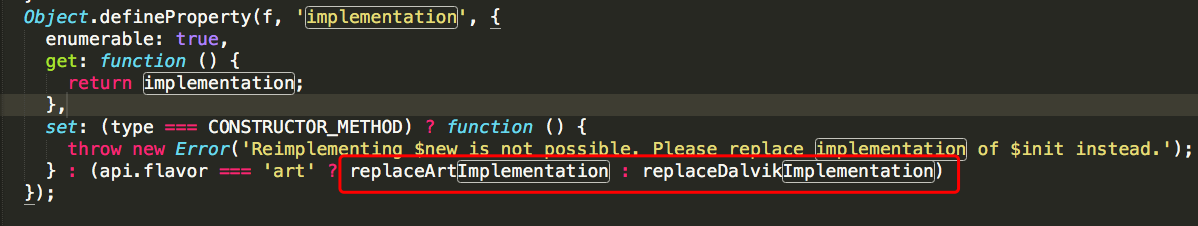
- implementation 区分了 ART 实现和 Dalvik 实现

Dalvik hook 实现
frida 兼容了低版本的 Android, 低于 Android 5.0 时,采用 Dalvik 虚拟机,其核心实现在 replaceDalvikImplementation 函数中。
frida 的 Dalvik hook 和 xposed 的 hook 原理相同,都是把要 hook 的 java 函数变成 native 函数,并修改函数的入口为自定义的内容,这样在调用时就会执行自定义的代码。
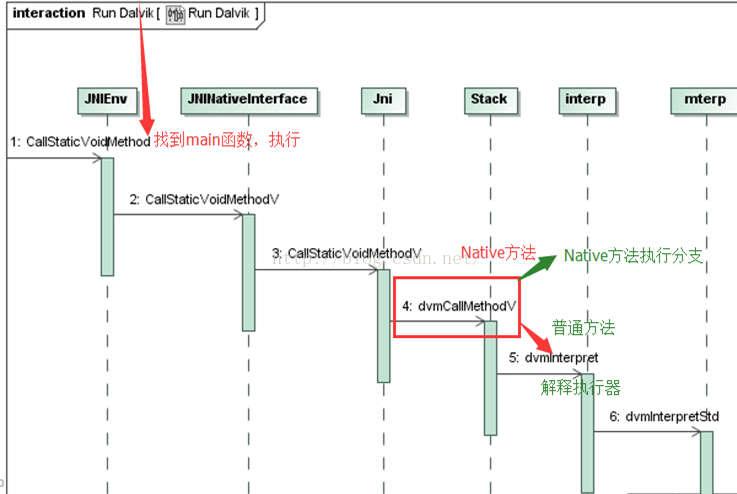
首先我们看一下 Dalvik 虚拟机执行 java 函数过程:

第 4 步 dvmCallMethodV 会根据 accessFlags 决定调用 native 还是 java 函数,因此修改 accessFlags 后,Dalvik 会认为这个函数是一个 native 函数,便走向了 native 分支。
Java 层的每一个函数在 Dalvik 中都对应一个 Method 数据结构,在源代码中定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| //https://android.googlesource.com/platform/dalvik/+/6d874d2bda563ada1034d2b3219b35d800fc6860/vm/oo/Object.h#418
struct Method {
ClassObject* clazz; /* method所属的类 public、native等*/
u4 accessFlags; /* 访问标记 */
u2 methodIndex; //method索引
//三个size为边界值,对于native函数,这3个size均等于参数列表的size
u2 registersSize; /* ins + locals */
u2 outsSize;
u2 insSize;
const char* name;//函数名称
/*
* Method prototype descriptor string (return and argument types)
*/
DexProto prototype;
/* short-form method descriptor string */
const char* shorty;
/*
* The remaining items are not used for abstract or native methods.
* (JNI is currently hijacking "insns" as a function pointer, set
* after the first call. For internal-native this stays null.)
*/
/* the actual code */
const u2* insns; /* instructions, in memory-mapped .dex */
/* cached JNI argument and return-type hints */
int jniArgInfo;
/*
* Native method ptr; could be actual function or a JNI bridge. We
* don't currently discriminate between DalvikBridgeFunc and
* DalvikNativeFunc; the former takes an argument superset (i.e. two
* extra args) which will be ignored. If necessary we can use
* insns==NULL to detect JNI bridge vs. internal native.
*/
DalvikBridgeFunc nativeFunc;
/*
* Register map data, if available. This will point into the DEX file
* if the data was computed during pre-verification, or into the
* linear alloc area if not.
*/
const RegisterMap* registerMap;
};
|
replaceDalvikImplementation 修改了 method 中的 accessFlags、registersSize、outsSize、insSize 和 jniArgInfo,将原 java 函数对应的结构体修改为一个 native 函数,并调用 dvmUseJNIBridge(
dvmUseJNIBridge 实现代码
)为这个 Method 设置一个 Bridge,改变结构体中的 nativeFunc,指向自定义的函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| function replaceDalvikImplementation (fn) {
if (fn === null && dalvikOriginalMethod === null) {
return;
}
//备份原来的method,
if (dalvikOriginalMethod === null) {
dalvikOriginalMethod = Memory.dup(methodId, DVM_METHOD_SIZE);
dalvikTargetMethodId = Memory.dup(methodId, DVM_METHOD_SIZE);
}
if (fn !== null) {
//自定的代码
implementation = implement(f, fn);
let argsSize = argTypes.reduce((acc, t) => (acc + t.size), 0);
if (type === INSTANCE_METHOD) {
argsSize++;
}
// 把method变成native函数
/*
* make method native (with kAccNative)
* insSize and registersSize are set to arguments size
*/
const accessFlags = (Memory.readU32(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_ACCESS_FLAGS)) | kAccNative) >>> 0;
const registersSize = argsSize;
const outsSize = 0;
const insSize = argsSize;
Memory.writeU32(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_ACCESS_FLAGS), accessFlags);
Memory.writeU16(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_REGISTERS_SIZE), registersSize);
Memory.writeU16(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_OUTS_SIZE), outsSize);
Memory.writeU16(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_INS_SIZE), insSize);
Memory.writeU32(methodId.add(DVM_METHOD_OFFSET_JNI_ARG_INFO), computeDalvikJniArgInfo(methodId));
//调用dvmUseJNIBridge为这个Method设置一个Bridge,本质上是修改结构体中的nativeFunc为自定义的implementation函数
api.dvmUseJNIBridge(methodId, implementation);
patchedMethods.add(f);
} else {
patchedMethods.delete(f);
Memory.copy(methodId, dalvikOriginalMethod, DVM_METHOD_SIZE);
implementation = null;
}
}
|
自定义的 js 代码如何生成?
implement 的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| function implement (method, fn) {
if (method.hasOwnProperty('overloads')) {
throw new Error('Only re-implementing a concrete (specific) method is possible, not a method "dispatcher"');
}
const C = method.holder; // eslint-disable-line
const type = method.type;
const retType = method.returnType;
const argTypes = method.argumentTypes;
const methodName = method.methodName;
const rawRetType = retType.type;
const rawArgTypes = argTypes.map((t) => (t.type));
const pendingCalls = method[PENDING_CALLS]; // eslint-disable-line
let frameCapacity = 2;
const argVariableNames = argTypes.map((t, i) => ('a' + (i + 1)));
const callArgs = argTypes.map((t, i) => {
if (t.fromJni) {
frameCapacity++;
return ['argTypes[', i, '].fromJni.call(self, ', argVariableNames[i], ', env)'].join('');
} else {
return argVariableNames[i];
}
});
let returnCapture, returnStatements, returnNothing;
if (rawRetType === 'void') {
returnCapture = '';
returnStatements = 'env.popLocalFrame(NULL);';
returnNothing = 'return;';
} else {
if (retType.toJni) {
frameCapacity++;
returnCapture = 'result = ';
returnStatements = 'var rawResult;' +
'try {' +
'if (retType.isCompatible.call(this, result)) {' +
'rawResult = retType.toJni.call(this, result, env);' +
'} else {' +
'throw new Error("Implementation for " + methodName + " expected return value compatible with \'" + retType.className + "\'.");' +
'}';
if (retType.type === 'pointer') {
returnStatements += '} catch (e) {' +
'env.popLocalFrame(NULL);' +
'throw e;' +
'}' +
'return env.popLocalFrame(rawResult);';
returnNothing = 'return NULL;';
} else {
returnStatements += '} finally {' +
'env.popLocalFrame(NULL);' +
'}' +
'return rawResult;';
returnNothing = 'return 0;';
}
} else {
returnCapture = 'result = ';
returnStatements = 'env.popLocalFrame(NULL);' +
'return result;';
returnNothing = 'return 0;';
}
}
let f;
eval('f = function (' + ['envHandle', 'thisHandle'].concat(argVariableNames).join(', ') + ') {' + // eslint-disable-line
'var env = new Env(envHandle, vm);' +
'if (env.pushLocalFrame(' + frameCapacity + ') !== JNI_OK) {' +
'return;' +
'}' +
'var self = ' + ((type === INSTANCE_METHOD) ? 'new C(thisHandle);' : 'new C(null);') +
'var result;' +
'var tid = Process.getCurrentThreadId();' +
'try {' +
'pendingCalls.add(tid);' +
'if (ignoredThreads[tid] === undefined) {' +
returnCapture + 'fn.call(' + ['self'].concat(callArgs).join(', ') + ');' +
'} else {' +
returnCapture + 'method.call(' + ['self'].concat(callArgs).join(', ') + ');' +
'}' +
'} catch (e) {' +
'env.popLocalFrame(NULL);' +
"if (typeof e === 'object' && e.hasOwnProperty('$handle')) {" +
'env.throw(e.$handle);' +
returnNothing +
'} else {' +
'throw e;' +
'}' +
'} finally {' +
'pendingCalls.delete(tid);' +
'}' +
returnStatements +
'};');
Object.defineProperty(f, 'methodName', {
enumerable: true,
value: methodName
});
Object.defineProperty(f, 'type', {
enumerable: true,
value: type
});
Object.defineProperty(f, 'returnType', {
enumerable: true,
value: retType
});
Object.defineProperty(f, 'argumentTypes', {
enumerable: true,
value: argTypes
});
Object.defineProperty(f, 'canInvokeWith', {
enumerable: true,
value: function (args) {
if (args.length !== argTypes.length) {
return false;
}
return argTypes.every((t, i) => (t.isCompatible(args[i])));
}
});
return new NativeCallback(f, rawRetType, ['pointer', 'pointer'].concat(rawArgTypes));
}
|
在自定义的代码里调用原函数?
ART hook 实现
frida 的 ART hook 实现也是把 java method 转为 native method, 但 ART 的运行机制不同于 Dalvik, 其实现也较为复杂,这里从 ART 运行机制开始解释。
ART 是一种代替 Dalivk 的新的运行时, 它具有更高的执行效率。ART 虚拟机执行 Java 方法主要有两种模式:quick code 模式和 Interpreter 模式。
- quick code 模式:执行 arm 汇编指令
- Interpreter 模式:由解释器解释执行 Dalvik 字节码
即使是在 quick code 模式中,也有类方法可能需要以 Interpreter 模式执行。反之亦然。解释执行的类方法通过函数 artInterpreterToCompiledCodeBridge 的返回值调用本地机器指令执行的类方法;本地机器指令执行的类方法通过函数 GetQuickToInterpreterBridge 的返回值调用解释执行的类方法;
ART 中的每一个函数都对应一个 ARTMethod 结构体,其中 entry_point_from_interpreter_ 和 entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ 分别表示两种模式的调用入口
ARTMethod 结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| //http://androidxref.com/8.1.0_r33/xref/art/runtime/art_method.h#708
class ArtMethod {
GcRoot<mirror::Class> declaring_class_; //method所属的class
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
GcRoot<mirror::PointerArray> dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
GcRoot<mirror::ObjectArray<mirror::Class>> dex_cache_resolved_types_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec.
uint32_t access_flags_;
/* Dex file fields. The defining dex file is available via declaring_class_->dex_cache_ */
// Offset to the CodeItem.
uint32_t dex_code_item_offset_;
// Index into method_ids of the dex file associated with this method.
uint32_t dex_method_index_;
/* End of dex file fields. */
// Entry within a dispatch table for this method. For static/direct methods the index is into
// the declaringClass.directMethods, for virtual methods the vtable and for interface methods the
// ifTable.
uint32_t method_index_;
// Fake padding field gets inserted here.
// Must be the last fields in the method.
// PACKED(4) is necessary for the correctness of
// RoundUp(OFFSETOF_MEMBER(ArtMethod, ptr_sized_fields_), pointer_size).
struct PACKED(4) PtrSizedFields {
// Method dispatch from the interpreter invokes this pointer which may cause a bridge into
// 以interpreter模式调用入口
void* entry_point_from_interpreter_;
void* entry_point_from_jni_; //jni函数入口
// 以quick code调用时的函数入口
void* entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
} ptr_sized_fields_;
}
|
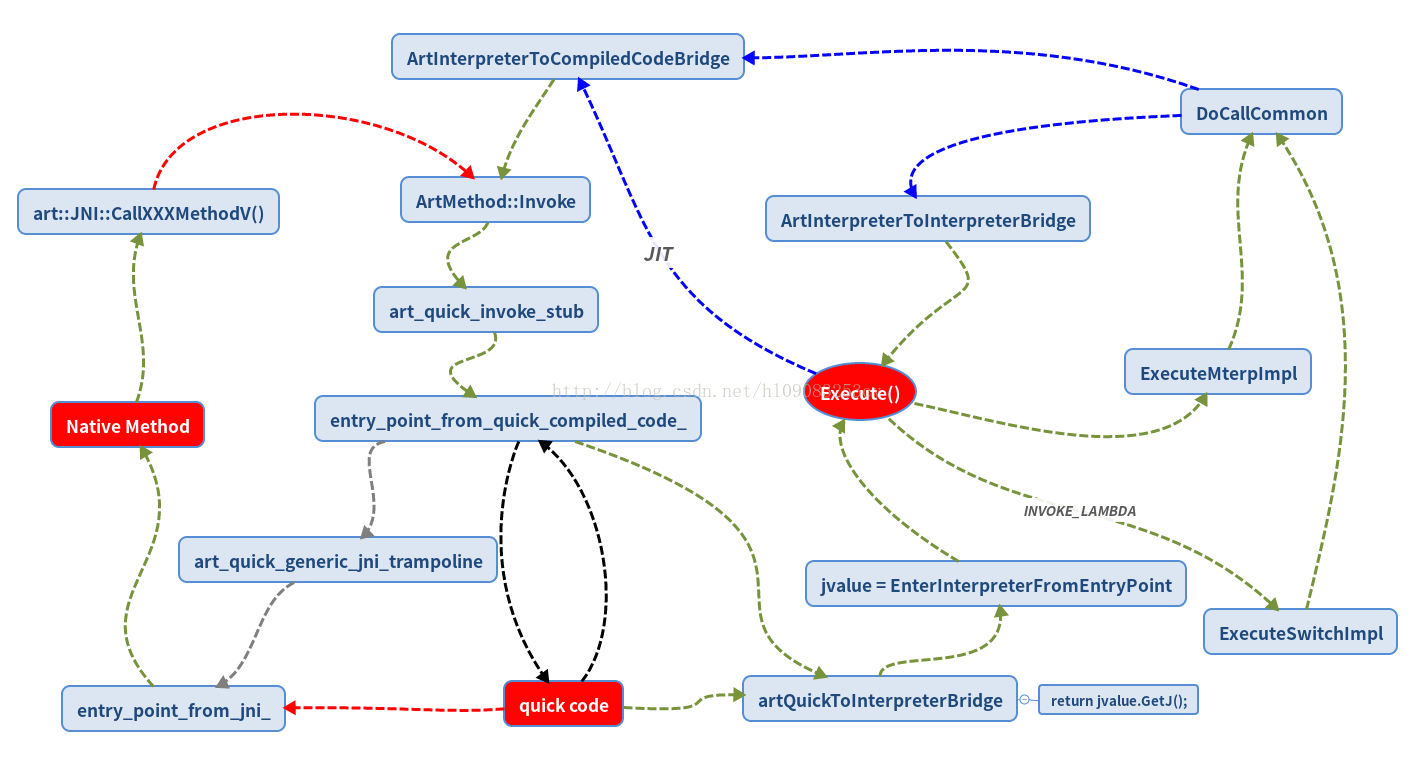
ART 的执行流程如下图:

如图所示,对于一个 native method, ART 虚拟机首先会尝试 quickcode 模式执行,检查 ARTMethod 结构中的 entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ 成员,这里分 3 种情况:
如果函数已经存在 quick code, 则指向这个函数对应的 quick code 的起始地址,而当 quick code 不存在时,它的值则会代表其他的意义;
当一个 java 函数不存在 quick code 时,它的值是函数 artQuickToInterpreterBridge 的地址,用以从 quick 模式切换到 Interpreter 模式来解释执行 java 函数代码;
当一个 java native(JNI)函数不存在 quick code 时,它的值是函数 art_quick_generic_jni_trampoline 的地址,用以执行没有 quick code 的 jni 函数;
因此,如果 frida 把一个 java method 改为 jni method, 显然是不存在 quick code,这时需要将 entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ 值修改为 art_quick_generic_jni_trampoline 的地址。
art_quick_generic_jni_trampoline 函数实现比较复杂(
代码分析
),主要负责 jni 调用的准备,包括堆栈的设置,参数的设置等, 该函数最终会调到 entry_point_from_jni_,即 jni 函数的入口。
因此,frida 把 java method 改为 jni method,需要修改 ARTMethod 结构体中的这几个值:
access_flags_ = native
entry_point_from_jni_ = 自定义代码的入口
entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ = art_quick_generic_jni_trampoline 函数的地址
entry_point_from_interpreter_ = artInterpreterToCompiledCodeBridge 函数地址
frida 对 ARTMethod 的修改在 replaceArtImplementation 函数中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| patchMethod(methodId, {
//jnicode入口entry_point_from_jni_改为自定义的代码
'jniCode': implementation,
//修改为access_flags_为native
'accessFlags': (Memory.readU32(methodId.add(artMethodOffset.accessFlags)) | kAccNative | kAccFastNative) >>> 0,
//entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_
'quickCode': api.artQuickGenericJniTrampoline,
//entry_point_from_interpreter_
'interpreterCode': api.artInterpreterToCompiledCodeBridge
});
|
patchMethod 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| function patchMethod (methodId, patches) {
const artMethodSpec = getArtMethodSpec(vm);
const artMethodOffset = artMethodSpec.offset;
Object.keys(patches).forEach(name => {
const offset = artMethodOffset[name];
if (offset === undefined) {
return;
}
const address = methodId.add(offset);
const suffix = (name === 'accessFlags' ? 'U32' : 'Pointer');
Memory['write' + suffix](address, patches[name]);
});
}
|
getArtMethodSpec 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| function _getArtMethodSpec (vm) {
const api = getApi();
let spec;
vm.perform(() => {
const env = vm.getEnv();
const process = env.findClass('android/os/Process');
const setArgV0 = env.getStaticMethodId(process, 'setArgV0', '(Ljava/lang/String;)V');
const runtimeModule = Process.getModuleByName('libandroid_runtime.so');
const runtimeStart = runtimeModule.base;
const runtimeEnd = runtimeStart.add(runtimeModule.size);
const apiLevel = getAndroidApiLevel();
const entrypointFieldSize = (apiLevel <= 21) ? 8 : pointerSize;
const expectedAccessFlags = kAccPublic | kAccStatic | kAccFinal | kAccNative;
let jniCodeOffset = null;
let accessFlagsOffset = null;
let remaining = 2;
for (let offset = 0; offset !== 64 && remaining !== 0; offset += 4) {
const field = setArgV0.add(offset);
if (jniCodeOffset === null) {
const address = Memory.readPointer(field);
if (address.compare(runtimeStart) >= 0 && address.compare(runtimeEnd) < 0) {
jniCodeOffset = offset;
remaining--;
}
}
if (accessFlagsOffset === null) {
const flags = Memory.readU32(field);
if (flags === expectedAccessFlags) {
accessFlagsOffset = offset;
remaining--;
}
}
}
if (remaining !== 0) {
throw new Error('Unable to determine ArtMethod field offsets');
}
const quickCodeOffset = jniCodeOffset + entrypointFieldSize;
const size = (apiLevel <= 21) ? (quickCodeOffset + 32) : (quickCodeOffset + pointerSize);
spec = {
size: size,
offset: {
jniCode: jniCodeOffset,
quickCode: quickCodeOffset,
accessFlags: accessFlagsOffset
}
};
if ('artInterpreterToCompiledCodeBridge' in api) {
spec.offset.interpreterCode = jniCodeOffset - entrypointFieldSize;
}
});
return spec;
}
|
参考:
- https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-229215.htm
- 基于 Frida 的全平台逆向分析
- Xposed 框架原理深入研究
- art_quick_generic_jni_trampoline 分析
- [ART Method Execution](
https://blog.csdn.net/hl09083253cy/article/details/78418702)
- [ART 执行类方法解析流程](
https://blog.csdn.net/zhu929033262/article/details/75093012)
- https://github.com/TinyNiko/TinyNiko.github.io/blob/master/Frida.pdf
- Creating a Java VM from Android Native Code
https://calebfenton.github.io/2017/04/05/creating_java_vm_from_android_native_code/
mac 下编译 frida
- git clone
https://github.com/frida/frida
- 创建代码签名证书 frida-cert
参考
https://sourceware.org/gdb/wiki/BuildingOnDarwin 中的 2.1.1
. Create a certificate 部分,将 gdb-cert 替换为 frida-cert 即可 - make
采坑记录:
ANDROID_NDK_ROOT must be set to the location of your r15c NDK.
解决办法:
设置环境变量 ANDROID_NDK_ROOT 为 ndk_r15c,必须为 r15 版本,我只是在当前 shell 里 export ANDROID_NDK_ROOT=/home/xxx/ndk-path 时无法编译通过,设为系统环境变量时,编译才通过。
Dependency ‘glib-2.0’ not found
1
2
| meson.build:123:0: ERROR: Dependency 'glib-2.0' not found, tried Extra Frameworks and Pkg-Config:
'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xe5 in position 16: invalid continuation byte
|
实际运行 pkg-config –modversion glib-2.0 时,发现 glib-2.0 是存在的,出现以上错误是因为路径中包含中文!!!
- AttributeError: module ‘enum’ has no attribute ‘IntFlag’
解决办法: 设置 PYTHONPATH 为 python3.6 的路径, export PYTHONPATH=/usr/bin/python3.6